Did you know that metabolic disorders increase the risk of developing serious health problems such as coronary heart disease, diabetes, and stroke? These conditions affect millions of people worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for understanding the risks associated with metabolic disorders and providing proper care and management. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of metabolic disorders, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowering you to enhance your metabolic health and reduce potential risks.
Key Takeaways:
- Metabolic disorders pose significant risks for developing chronic health conditions.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of metabolic disorders is crucial for early detection and intervention.
- Proactive management and lifestyle choices play a vital role in reducing the impact of metabolic disorders.
- Proper treatment, through medication and lifestyle modifications, can improve metabolic health.
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for managing metabolic disorders effectively.
What Is a Metabolic Disorder?
A metabolic disorder is a condition that affects the body’s ability to process and utilize nutrients, leading to abnormal chemical reactions and disruptions in overall metabolic function. These disorders can result in a wide range of symptoms and complications, highlighting the need for early detection and management.
There are various types of metabolic disorders, including but not limited to:
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Inherited metabolic disorders
Each type of metabolic disorder has its own unique characteristics and impact on the body’s metabolic processes. Early detection and intervention are crucial for effective management and reducing the potential risks associated with these disorders.
Identifying the Signs of Metabolic Disorders
Identifying the signs and symptoms of metabolic disorders is crucial for early detection and intervention. By recognizing these signs, you can seek prompt medical attention and take steps to manage your metabolic health effectively.
Large Waistline and Body Shape
A large waistline or an apple-shaped body is a common sign of metabolic disorders, particularly abdominal obesity. This indicates an accumulation of visceral fat around the abdominal area, which is associated with an increased risk of developing heart disease. To determine if you have a large waistline, measure the circumference around your waist at the level of your belly button. Generally, a waist circumference of more than 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men is considered large and may indicate a metabolic disorder.

Recognizing Symptoms Related to High Blood Sugar
Symptoms related to high blood sugar levels can also be indicative of a metabolic disorder. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation:
- Increased thirst: Feeling excessively thirsty even after drinking fluids.
- Frequent urination: Having to urinate more often than usual.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or lacking energy, even after adequate rest.
- Blurred vision: Experiencing blurry or impaired vision.
These symptoms may suggest high blood sugar levels, which can be an indication of metabolic disorders such as diabetes. Timely recognition of these symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Impact of Metabolic Disorders on Your Health
Metabolic disorders can have a significant impact on your overall health. One such disorder is metabolic syndrome, which is closely connected to the development of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Understanding the relationship between metabolic disorders and these conditions is crucial for taking proactive steps to manage your health effectively.
Connecting Metabolic Syndrome with Diabetes and Heart Disease
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These factors increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Individuals with metabolic syndrome are twice as likely to develop heart disease and five times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those without the syndrome.
Understanding Long-Term Complications
In addition to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease, metabolic disorders can lead to various long-term complications. These complications include kidney disease, neuropathy (nerve damage), and diabetic retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels of the retina). Early detection and proper management of metabolic disorders are crucial in minimizing the risk of these complications.
Metabolic Disorder: Risk Factors You Should Know
Several risk factors contribute to the development of metabolic disorders. These include:
- Age: Advancing age increases the risk of metabolic disorders.
- Ethnicity: Certain populations, such as African-Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, have a higher risk of developing metabolic disorders.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor for metabolic disorders.
- Diabetes during Pregnancy: Gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, can increase the risk of metabolic disorders in both the mother and child.
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
- Sleep Apnea: This sleep disorder has been linked to an elevated risk of metabolic disorders.
Being aware of these risk factors can facilitate early intervention and the implementation of preventive measures. Understanding your individual risk profile can help you make informed decisions about your lifestyle, take proactive steps to manage your metabolic health, and reduce the likelihood of developing metabolic disorders.
It is important to note that these risk factors may vary based on individual circumstances, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized guidance.
| Risk Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Advancing age increases the risk of metabolic disorders. |
| Ethnicity | Certain populations, such as African-Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, have a higher risk of developing metabolic disorders. |
| Obesity | Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor for metabolic disorders. |
| Diabetes during Pregnancy | Gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, can increase the risk of metabolic disorders in both the mother and child. |
| Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease | Presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disorders. |
| Sleep Apnea | This sleep disorder has been linked to an elevated risk of metabolic disorders. |
Lifestyle Choices to Combat Metabolic Disorders
Making positive lifestyle choices is crucial in managing metabolic disorders. By adopting healthy habits, individuals can improve their metabolic health and reduce the risks associated with these conditions.
The Role of Diet in Managing Metabolic Health
A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining metabolic health. It is essential to consume a variety of nutritious foods, including:
- Fruits – Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits provide essential nutrients to support metabolic function.
- Vegetables – Packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, vegetables help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
- Lean Proteins – Sources of lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, tofu, and beans, provide essential amino acids for muscle development and metabolic regulation.
- Whole Grains – Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread contain fiber and nutrients that support healthy digestion and stabilize blood sugar levels.
It is important to limit intake of saturated fats and salt, as they can have a negative impact on metabolic health. Choosing healthier cooking methods, such as grilling, steaming, or baking, can also improve the nutritional value of meals.
The Importance of Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing metabolic disorders. Exercise offers numerous benefits, including:
- Weight Control – Physical activity helps burn calories and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity and related metabolic complications.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity – Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to effectively use glucose for energy.
- Enhanced Metabolic Function – Physical activity stimulates metabolic processes, promoting efficient nutrient utilization and overall metabolic health.
It is recommended to incorporate a combination of aerobic exercises (such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming) and strength training activities (such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises) into a weekly routine for optimal outcomes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with muscle-strengthening activities at least twice a week.

By making conscious choices to follow a healthy diet and engage in regular physical activity, individuals can effectively manage metabolic disorders and improve their overall metabolic health.
Metabolic Disorders Treatment Options
The treatment of metabolic disorders involves a comprehensive approach tailored to the specific condition and individual needs. Treatment options may include medication to manage blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure, as well as lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. In some cases, surgery or other interventions may be necessary. A healthcare professional will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific metabolic disorder and its severity.
Understanding and Managing Blood Glucose Levels
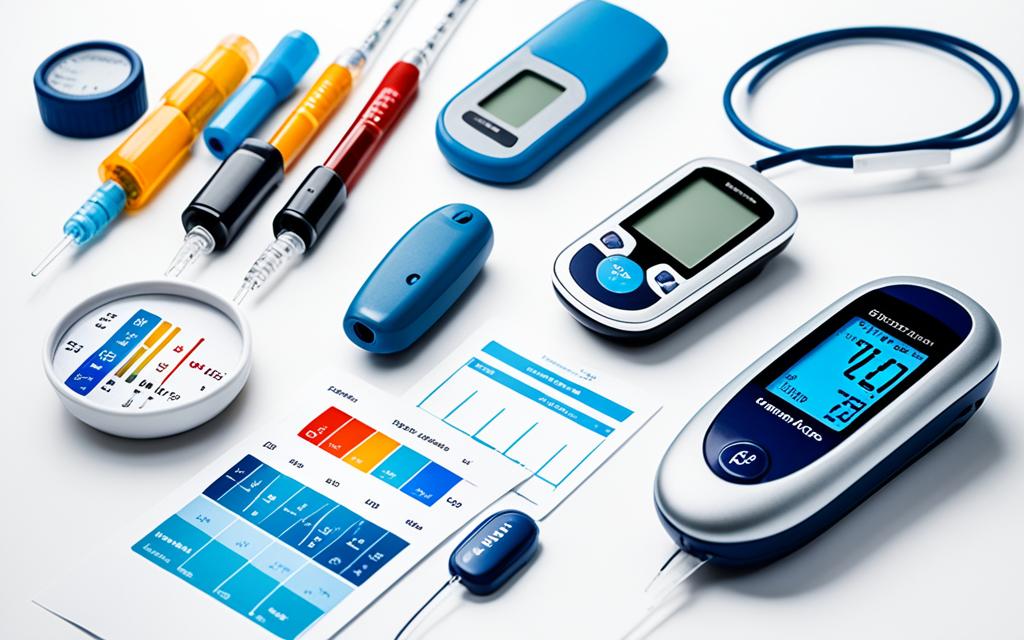
Tools for Monitoring: Glucometer and Continuous Blood Glucose Monitor
Monitoring and managing blood glucose levels are critical for individuals with metabolic disorders like diabetes. To effectively track blood sugar levels, two commonly used tools are the glucometer and the continuous blood glucose monitor.
The glucometer is a portable device that measures blood glucose levels using a small blood sample obtained through a finger prick. It provides immediate results, allowing individuals to make real-time decisions regarding their treatment and lifestyle choices.
The continuous blood glucose monitor, on the other hand, provides continuous and real-time monitoring of blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. It consists of a small sensor inserted under the skin, which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The data collected by the sensor is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone, providing individuals with a comprehensive view of their blood glucose patterns.
Both tools play a crucial role in helping individuals with metabolic disorders understand their blood glucose levels and make informed decisions to manage their health effectively.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Glucose Levels
Achieving and maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with metabolic disorders. Alongside monitoring tools, implementing the following strategies can contribute to optimal blood sugar management:
- Adopting a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive carbohydrate intake can help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Incorporating regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity regularly can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing for better utilization of glucose by the body’s cells. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Adhering to medication regimens: If prescribed medication to manage blood glucose levels, it is crucial to take them as directed by a healthcare professional. Medications such as insulin or oral antidiabetic agents can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Practicing stress management: Stress can impact blood glucose levels. Engaging in relaxation techniques or activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies can help reduce stress and promote better blood sugar control.
By combining these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy blood glucose levels and effectively managing their metabolic health.
Metabolic Disorders in Adults vs. Children
Metabolic disorders can affect individuals of all ages, but there are differences in symptoms and treatment approaches between adults and children. Distinguishing the symptoms and proper diagnosis is essential for effective management. Additionally, special considerations need to be taken into account when dealing with metabolic syndrome in children, as their treatment and lifestyle adjustments may differ from adults.
Distinguishing Symptoms and Treatments
Metabolic disorders may present differently in adults compared to children. In adults, common symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight changes, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. On the other hand, children with metabolic disorders may display symptoms such as delayed growth, feeding difficulties, developmental delays, low muscle tone, and altered behavior.
The treatment approaches for metabolic disorders in adults and children also differ. In adults, management typically involves lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and medication to control blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure levels. In children, the treatment approach may vary depending on the specific metabolic disorder and its associated symptoms. It often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including dietary modifications, physical therapy, medication, and close monitoring of growth and developmental milestones.
Special Considerations for Children with Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of metabolic disorders including obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, can also affect children. However, treating metabolic syndrome in children requires specific considerations.
For children with metabolic syndrome, lifestyle interventions are essential, focusing on promoting healthy eating habits and increasing physical activity. These interventions may involve age-appropriate dietary modifications, encouraging regular exercise, and setting realistic goals for weight management.
Moreover, it is crucial to involve the child’s family and provide support and education to both the child and their parents or caregivers. By working collaboratively, healthcare professionals can help children with metabolic syndrome make sustainable lifestyle changes and reduce their risk of long-term complications.

The Intricacies of Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosis
Diagnosing metabolic syndrome involves a comprehensive evaluation of various factors such as waist circumference, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels. Healthcare professionals may conduct physical examinations, order blood tests, and use established diagnostic criteria to determine the presence of metabolic syndrome. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in preventing complications and implementing appropriate treatment strategies.

Proper diagnosis of metabolic syndrome requires a thorough assessment of key indicators. Healthcare professionals will measure waist circumference to determine abdominal obesity, as excess fat around the waist is a significant risk factor for metabolic syndrome. Blood pressure measurements are taken to detect high blood pressure levels, which are often associated with the condition. Additionally, blood tests are conducted to analyze fasting glucose levels, lipid profile (including cholesterol and triglycerides), and other relevant biomarkers.
The diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome may vary slightly depending on the specific guidelines followed by healthcare professionals. The most commonly used criteria include those established by organizations such as the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the American Heart Association (AHA). These criteria typically consider a combination of the aforementioned factors, with specific cutoff values for each indicator.
It is crucial to remember that metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors that often occur together, and its diagnosis requires the presence of a specific number of risk factors as defined by the diagnostic criteria.
The diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is an important step in addressing and managing this condition. Once diagnosed, individuals can work with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet and increasing physical activity, and potentially medication to manage specific risk factors. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to assess progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
| Indicators | Cutoff Values |
|---|---|
| Waist Circumference | Men: >40 inches Women: >35 inches |
| Blood Pressure | >130/85 mmHg |
| Fasting Glucose | >100 mg/dL (or being treated for diabetes) |
| Triglycerides | >150 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | Men: <40 mg/dL Women: <50 mg/dL |
Table: Diagnostic Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome
Preventing Metabolic Syndrome Through Proactive Measures
Taking proactive measures can help prevent the development or progression of metabolic syndrome. By adopting a prediabetes diet and regularly taking diabetes tests, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with metabolic disorders and maintain your metabolic health.
Adopting a Prediabetes Diet to Curtail Risks
To prevent metabolic syndrome, it is crucial to adopt a prediabetes diet. This diet focuses on healthy eating habits and portion control, which can help regulate blood sugar levels, manage weight, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It involves consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated fats and added sugars. By making these dietary changes, you can curb the risks associated with metabolic disorders and support overall metabolic health.
Regular Diabetes Tests and the Significance of A1C
Regular diabetes tests are crucial for preventing metabolic syndrome and maintaining metabolic health. These tests can provide valuable insights into your blood sugar control and help identify any early indications of prediabetes or diabetes. Regular monitoring allows you to take appropriate actions, such as adjusting your diet, increasing physical activity, or working with your healthcare provider to implement necessary treatment options. One of the significant tests for monitoring diabetes is the A1C test. This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, providing an essential indicator of your overall metabolic health. By regularly checking your A1C levels, you can gauge the effectiveness of your lifestyle choices and make informed decisions to maintain healthy blood sugar control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metabolic disorders are complex conditions that require comprehensive care and management. It is crucial for individuals to understand the risks, symptoms, and treatment options associated with metabolic disorders in order to take control of their metabolic health and reduce the potential complications.
By making informed lifestyle choices, such as adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can improve their overall metabolic well-being. Monitoring blood glucose levels through the use of tools like glucometers and continuous blood glucose monitors can further aid in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and managing metabolic disorders effectively.
Furthermore, working closely with healthcare professionals is essential in developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses specific metabolic disorders and their severity. Through collaboration with healthcare professionals, individuals can receive the appropriate medication, lifestyle modifications, and surgical interventions, if necessary, to effectively manage their metabolic disorders and prevent long-term complications.
To improve metabolic health and lead a healthier life, it is important to stay proactive and take charge of managing metabolic disorders. By implementing the key takeaways discussed in this article, you can enhance your metabolic well-being and reduce the potential risks associated with metabolic disorders.
FAQ
What is a metabolic disorder?
What are the signs of metabolic disorders?
How do metabolic disorders impact health?
What are the risk factors for metabolic disorders?
What lifestyle choices can help manage metabolic disorders?
What are the treatment options for metabolic disorders?
How can blood glucose levels be monitored and managed?
Are there differences in metabolic disorders between adults and children?
How is metabolic syndrome diagnosed?
Can metabolic syndrome be prevented?
Source Links
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/metabolic-syndrome
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/metabolic-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20351916
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/metabolic-syndrome/about-metabolic-syndrome


