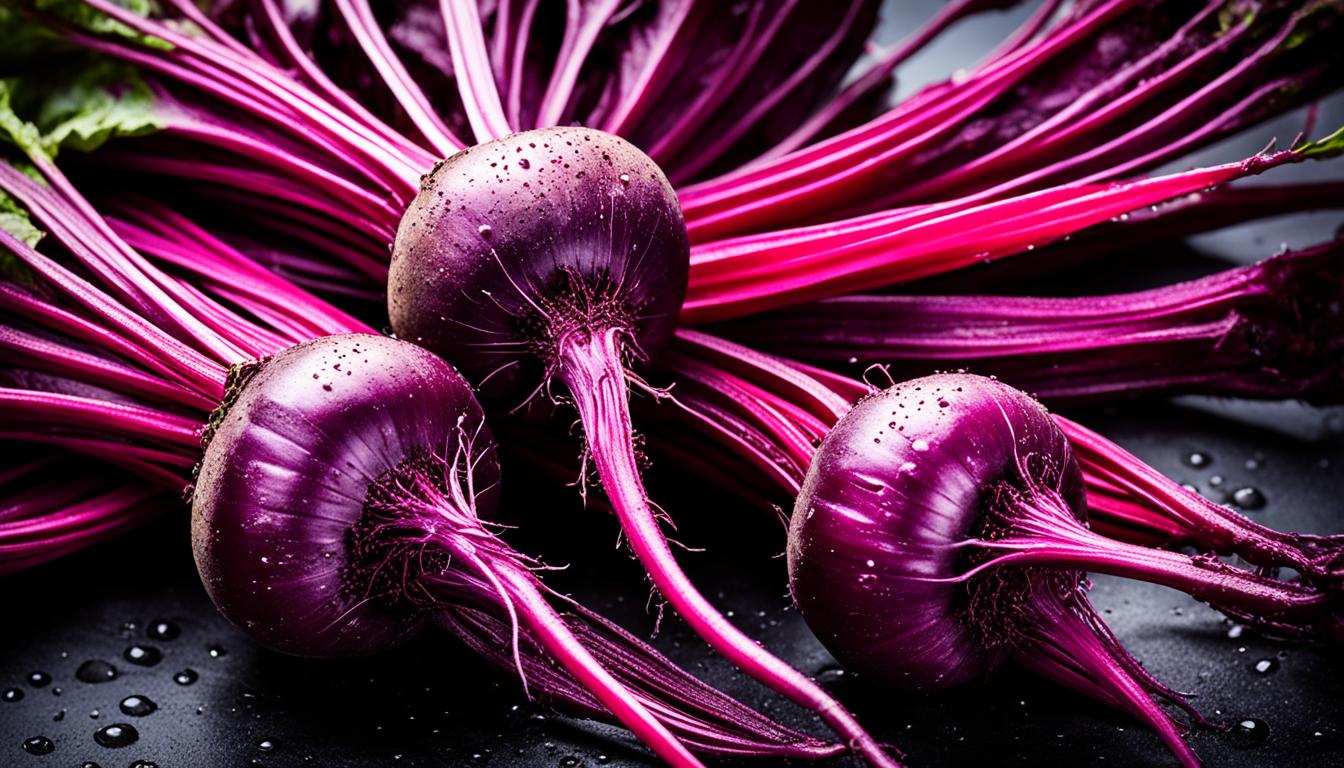
Beetroots are mostly water (87%), with carbs being the next big part (8%). They also have a good amount of fiber (2-3%). This mix makes beetroots a top food loaded with vitamins, minerals, and healthy plant stuff. Beetroots (Beta vulgaris), sometimes called red beets, table beets, or garden beets, do amazing things for your health. They can make your heart healthier, lower your blood pressure, and help you do more when you exercise.
Beetroots are full of important nutrients. They are a key source of fiber, folate (which is vitamin B9), manganese, potassium, iron, and vitamin C. A cup of boiled beetroot has less than 60 calories. Meanwhile, 3/4 cup of raw beets has 43 calories and is mostly water. They also pack some protein, carbs, sugar, and fiber, and almost no fat.
Beetroots and beetroot juice are great for you. They help improve your blood flow, lower blood pressure, and boost your exercise ability. Much of this comes from their high inorganic nitrates. These nitrates change to nitric oxide in your body. This happens and makes your blood vessels open up and relax.
Key Takeaways
- Beetroots are a highly nutritious root vegetable, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and beneficial plant compounds.
- Beetroots are a good source of fiber, folate, manganese, potassium, iron, and vitamin C.
- The health benefits of beetroots include improved heart health, lower blood pressure, and enhanced exercise performance.
- Beetroots are rich in inorganic nitrates, which can be converted into nitric oxide, promoting vasodilation and lowering blood pressure.
- Beetroots contain unique plant compounds like betanin and betalains, which possess anti-inflammatory properties.
Introduction to Beet Roots
Beetroots, or beet roots, are known for their bold colors and unique taste. They are loved for their deep, earthy taste and scent. Many people call them a superfood because they are very nutritious. Beets are not just red; you can find them in yellow, white, and rainbow colors too.
What are Beet Roots?
Beet roots are the main part of the beet plant, found underground. They are a type of root vegetable. You can eat them in many ways, including raw, juiced, roasted, steamed, or pickled. People like them for their special taste and for being healthy.
Varieties of Beet Roots
There are many types of beet roots. They come in different colors. Some popular ones are:
- Red beets: The classic deep purple-red beets
- Golden beets: Bright yellow or orange in color
- White beets: Pale white or ivory-colored roots
- Rainbow beets: A mix of red, yellow, and white beets
Each color variety of beet root has its own taste, feel in the mouth, and nutrition. This makes them great for cooking or eating healthy.
Beet Roots Nutrition Facts
Calories and Macronutrients
Beets are packed with water (87%), carbs (8%), and some fiber (2–3%). A boiled cup of beetroot has less than 60 calories. Meanwhile, a 3/4 cup of raw beets (about 100 grams) is rich in folate, manganese, potassium, iron, and vitamin C. The main carbs in beetroot are simple sugars like glucose and fructose. Despite being high in fiber, beets have FODMAPs, which might upset some stomachs.
Vitamins and Minerals
Beetroots shine in providing folate (vitamin B9), manganese, potassium, iron, and vitamin C. Beets’ fibrous nature means each 3/4-cup serves up 2–3 grams of fiber. Moreover, a 3.5-ounce beetroot serving contains 44 calories, 1.7 grams of protein, and 2 grams of fiber. This vegetable is notably rich in folate, manganese, copper, potassium, magnesium, vitamin C, and vitamin B6.
| Nutrient | Amount per 3.5-ounce (100g) serving | Percent of Daily Value (DV) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 44 | – |
| Protein | 1.7 grams | – |
| Fat | 0.2 grams | – |
| Carbohydrates | 10 grams | – |
| Fiber | 2 grams | – |
| Folate | – | 20% of the DV |
| Manganese | – | 14% of the DV |
| Copper | – | 8% of the DV |
| Potassium | – | 7% of the DV |
| Magnesium | – | 6% of the DV |
| Vitamin C | – | 4% of the DV |
| Vitamin B6 | – | 4% of the DV |
| Iron | – | 4% of the DV |
Unique Plant Compounds in Beet Roots
Beetroots feature key plant compounds like betanin and inorganic nitrates. Betanin, also known as beetroot red, gives beets their strong red color. It’s linked to various health benefits.
Betanin
Betanin is the main pigment in beetroots, making them red. It’s said to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These could lead to health gains from eating beets.
Inorganic Nitrates
Beetroots and beetroot juice are rich in inorganic nitrates. These nitrates can turn into nitric oxide in our bodies. This process plays a role in lowering blood pressure and maybe boosting exercise results.
Health Benefits of Beet Roots
Beetroots are colorful and packed with good nutrients. They do a lot for your health. They help lower blood pressure, boost your exercise power, and fight inflammation. This veggie is full of things your body needs.
Lowering Blood Pressure
Beet root health benefits include bringing down blood pressure. Beets can lower your blood pressure by 3–10 mm Hg in a few hours. They do this by increasing nitric oxide, which helps your blood vessels open up. As a result, your blood can flow better.
Enhancing Exercise Performance
Beets improve exercise performance thanks to their dietary nitrates. These nitrates support your muscles, making your body more efficient. They can boost how much oxygen your body uses by 20%. This leads to better stamina and exercise ability.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Beetroots have a special pigment called betalains. These pigments help fight inflammation, which is linked to many serious illnesses. Beets can help with conditions like obesity and heart disease. This is because they have a lot of these special compounds.
beet roots nutrition facts
Beets have a great nutritional value. They are low in calories but packed with essential beet root nutrition facts and nutrients in beets. In 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of boiled beetroot, you’ll find 44 calories. It also has 1.7 grams of protein, 0.2 grams of fat, 10 grams of carbs, and 2 grams of fiber. Beets are full of folate, manganese, copper, potassium, magnesium, vitamin C, and vitamin B6.
| Nutrient | Amount per 3.5 oz (100g) serving |
|---|---|
| Calories | 44 |
| Protein | 1.7 g |
| Fat | 0.2 g |
| Carbs | 10 g |
| Fiber | 2 g |
| Folate (Vitamin B9) | 20% DV |
| Manganese | 14% DV |
| Copper | 8% DV |
| Potassium | 7% DV |
Beets provide essential beet nutritional value. They are a source of vitamins like Vitamin C and Vitamin B6. Plus, they offer minerals such as magnesium and iron. The great beet root nutrition facts show why beets are key for a healthy eating plan.
Potential Side Effects
While beetroots are usually fine to eat, they have some compounds that might not sit well with everyone. It’s important to know about these side effects. This helps make sure you eat beetroots in a safe way.
Oxalates and Kidney Stones
Beetroots are high in oxalates. This can lead to kidney stone formation especially in people who already get them. If you have had kidney stones before, you might want to be careful with how much of the plant you eat.
FODMAPs and Digestive Issues
Beets have FODMAPs, which can upset the stomach in some people. This is true for those with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or just very sensitive stomachs. Fructans in beetroot can cause bloating, gas, or stomach pains in these folks.
If you know you already have issues with certain foods, it’s smart to talk to a doctor before adding beetroots to your meals. They can offer advice to help you eat beet root safely and avoid potential problems.
Incorporating Beet Roots into Your Diet
Beets are not only nutritious but also tasty. When picking beet roots, go for those that are heavy and have bright, green tops. To keep them fresh, put them in the fridge in a sealed bag. They’ll stay crispy and colorful this way.
Selecting and Storing Beet Roots
Choose beets that look good and feel firm when buying and storing beet roots. Make sure the greens are fresh, not wilted. Keep them in the fridge in a bag or with a damp paper towel. They will last for about two weeks like this.
Cooking Methods and Recipes
There are many ways to prepare beets. You can roast, steam, boil, or pickle them. They are also tasty when raw, like in salads. Try dishes such as balsamic roasted beets, beet hummus, and beet fries to add them to your meals. Beet juice is a nutritious drink you might enjoy as well.
Beet Roots for Specific Health Conditions
Beet Roots and Diabetes
Beets have an antioxidant named alpha-lipoic acid. It might lower glucose levels and help the body use insulin better, which is good for beet roots for diabetes. Some early studies think beets, especially a compound called betalain, could fight cancer by stopping harmful cell changes. But, we need more research to be sure of these benefits.
Beet Roots and Cancer Prevention
Beets contain compounds like betaine, ferulic acid, and kaempferol. These may help prevent cancer, though more studies are necessary to confirm this. Beets are also full of fiber, aiding in good digestion and lowering the risk of colon cancer. The anti-inflammatory features of betalains could support heart, liver, and joint health, too.
While we’re still learning about how beets help with diabetes and cancer, they’re undeniably good for you. Adding them to your diet can boost your health overall.
Conclusion
Beetroots are packed with nutrition and can bring many health perks. They’re rich in vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds like betanin and nitrates. These beet roots help with lowering blood pressure, boosting exercise, and fighting off inflammation.
However, not everyone should have beet roots. They have oxalates and FODMAPs that might not sit well with some people. Yet, for most, adding beet roots to meals can up your nutrient game and better your health.
The good stuff in beet roots shines through their nutrition. They can lower blood pressure, amp up exercise, and squash inflammation. All these benefits show why beet roots are a great fit for a health-conscious life.
FAQ
What are the key nutrients found in beet roots?
What are the potential health benefits of consuming beet roots?
Are there any potential side effects of eating beet roots?
How can beet roots be incorporated into a healthy diet?
Can beet roots benefit individuals with diabetes or cancer?
Source Links
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods/beetroot
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/benefits-of-beets
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/277432
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6947971/
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-306/beet
- https://nutrigardens.com/blogs/blog/beetroot-side-effects-and-reactions
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-beetroot
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8565237/